This package provides methods for obtaining estimated marginal means (EMMs, also known as least-squares means) for factor combinations in a variety of models. Supported models include [generalized linear] models, models for counts, multivariate, multinomial and ordinal responses, survival models, GEEs, and Bayesian models. For the latter, posterior samples of EMMs are provided. The package can compute contrasts or linear combinations of these marginal means with various multiplicity adjustments. One can also estimate and contrast slopes of trend lines. Some graphical displays of these results are provided.
Overview
- Vignettes
A number of vignettes are provided to help the user get acquainted with the emmeans package and see some examples.
- Concept
Estimated marginal means (see Searle et al. 1980 are popular for summarizing linear models that include factors. For balanced experimental designs, they are just the marginal means. For unbalanced data, they in essence estimate the marginal means you would have observed that the data arisen from a balanced experiment. Earlier developments regarding these techniques were developed in a least-squares context and are sometimes referred to as “least-squares means”. Since its early development, the concept has expanded far beyond least-squares settings.
- Reference grids
The implementation in emmeans relies on our own concept of a reference grid, which is an array of factor and predictor levels. Predictions are made on this grid, and estimated marginal means (or EMMs) are defined as averages of these predictions over zero or more dimensions of the grid. The function
ref_gridexplicitly creates a reference grid that can subsequently be used to obtain least-squares means. The object returned byref_gridis of class"emmGrid", the same class as is used for estimated marginal means (see below).Our reference-grid framework expands slightly upon Searle et al.'s definitions of EMMs, in that it is possible to include multiple levels of covariates in the grid.
- Models supported
As is mentioned in the package description, many types of models are supported by the package. See vignette("models", "emmeans") for full details. Some models may require other packages be installed in order to access all of the available features. For models not explicitly supported, it may still be possible to do basic post hoc analyses of them via the
qdrgfunction.- Estimated marginal means
The
emmeansfunction computes EMMs given a fitted model (or a previously constructedemmGridobject), using a specification indicating what factors to include. Theemtrendsfunction creates the same sort of results for estimating and comparing slopes of fitted lines. Both return anemmGridobject.- Summaries and analysis
The
summary.emmGridmethod may be used to display anemmGridobject. Special-purpose summaries are available viaconfint.emmGridandtest.emmGrid, the latter of which can also do a joint test of several estimates. The user may specify by variables, multiplicity-adjustment methods, confidence levels, etc., and if a transformation or link function is involved, may reverse-transform the results to the response scale.- Contrasts and comparisons
The
contrastmethod foremmGridobjects is used to obtain contrasts among the estimates; several standard contrast families are available such as deviations from the mean, polynomial contrasts, and comparisons with one or more controls. AnotheremmGridobject is returned, which can be summarized or further analyzed. For convenience, apairs.emmGridmethod is provided for the case of pairwise comparisons.- Graphs
The
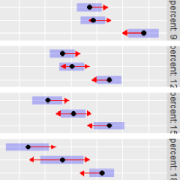
plot.emmGridmethod will display side-by-side confidence intervals for the estimates, and/or “comparison arrows” whereby the *P* values of pairwise differences can be observed by how much the arrows overlap. Theemmipfunction displays estimates like an interaction plot, multi-paneled if there are by variables. These graphics capabilities require the lattice package be installed.- MCMC support
When a model is fitted using MCMC methods, the posterior chains(s) of parameter estimates are retained and converted into posterior samples of EMMs or contrasts thereof. These may then be summarized or plotted like any other MCMC results, using tools in, say coda or bayesplot.
- multcomp interface
The
as.glhtfunction andglhtmethod foremmGrids provide an interface to theglhtfunction in the multcomp package, thus providing for more exacting simultaneous estimation or testing. The package also provides anemmfunction that works as an alternative tomcpin a call toglht.